
At Home Owners Association, we understand that homeowners are increasingly interested in solar energy solutions. The potential for significant long-term savings and environmental benefits makes solar an attractive option for many.
However, one of the most common questions we receive is about the cost of solar energy for home. This comprehensive guide will break down the factors affecting solar energy prices, average system costs, and available financial incentives to help you make an informed decision.
What Impacts Solar Energy Costs?
Solar energy costs vary significantly based on several key factors. These elements influence the final price tag of solar installations across Australia.
Panel Technology and Efficiency
Solar panel technology plays a major role in determining system costs. Monocrystalline panels, known for their higher efficiency, typically cost more. Premium panels like SunPower can cost over $700 each, while budget-friendly options such as Jinko are around $130 per panel. The choice between these can lead to a difference of more than $13,000 for a typical 10 kW system.
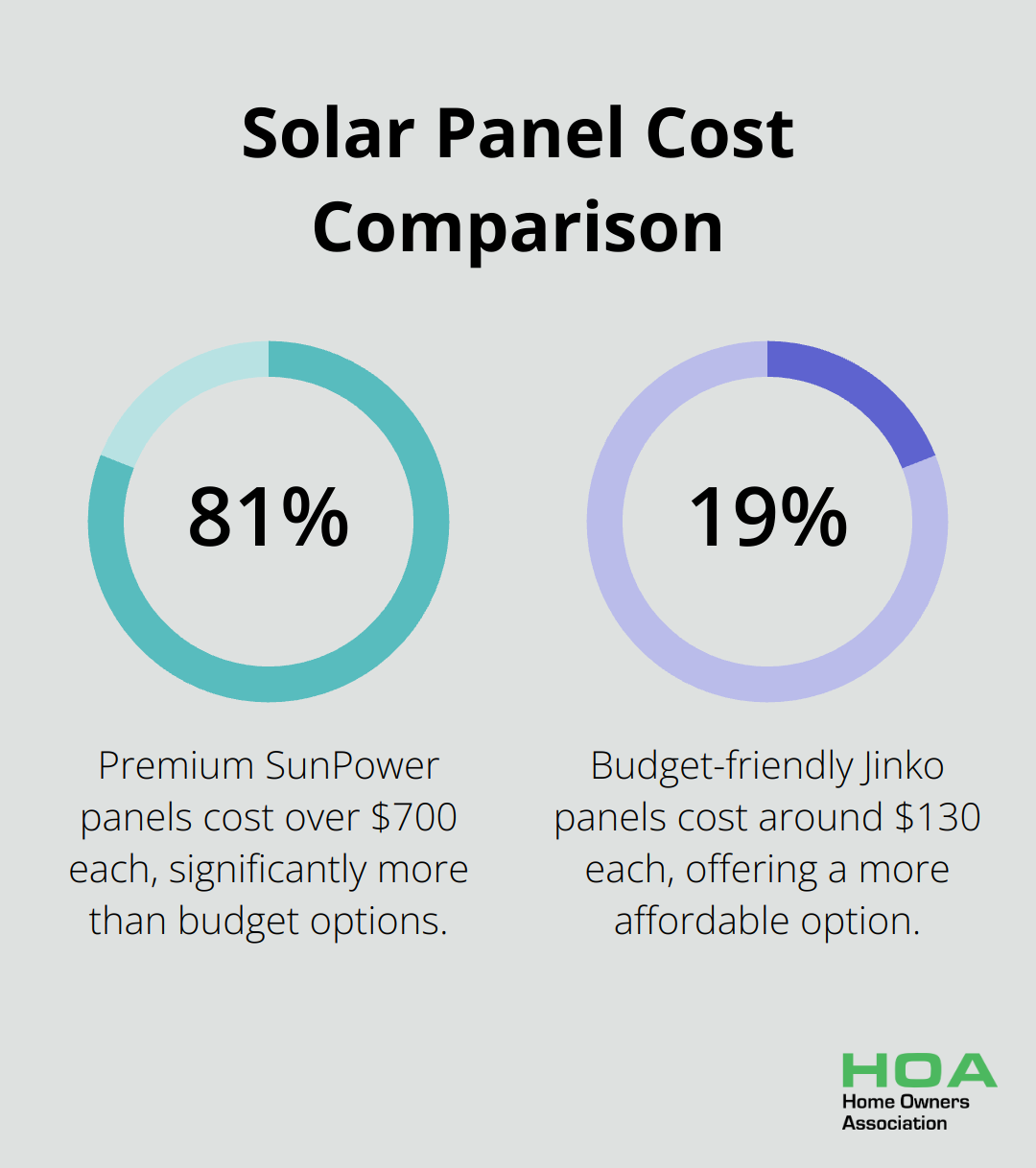
Higher efficiency panels produce more energy, which benefits homes with limited roof space or partial shading. However, it’s important to balance the increased upfront cost against long-term energy production.
Roof Characteristics and Installation Complexity
Your roof’s size, shape, and condition significantly impact installation costs. A larger roof area might require more panels, increasing overall expenses. Complex roof designs with multiple angles or obstructions (like chimneys and vents) can complicate installation, leading to higher labour costs.
The roof’s structural integrity is another important factor. Older roofs might need reinforcement or repairs before solar panel installation, adding to the total project cost. A professional assessment of your roof before committing to solar installation is advisable.
Geographic Factors and Sunlight Exposure
Australia’s diverse climate means solar energy potential varies across regions. Northern areas generally receive more sunlight, potentially requiring fewer panels to meet energy needs. However, installation costs in remote areas can be higher due to travel and accommodation expenses for installers.
Local weather patterns also affect costs. Areas prone to extreme heat might require more durable, heat-resistant panels, which can increase costs. On the flip side, these regions often see higher energy production, potentially offsetting the initial investment more quickly.
Electricity Rates and Energy Consumption
Your current electricity rates and consumption patterns are important in determining the cost-effectiveness of solar energy. Areas with higher electricity prices often see faster returns on solar investments. For example, a household in South Australia (where electricity rates are among the highest in the country) might see a quicker payback period compared to a similar system in Tasmania.
Understanding your energy usage is key. A typical Australian home uses between 15-20 kWh per day. Sizing your system to match this consumption can optimise your investment. Over-sizing a system might lead to excess production that isn’t fully utilised, especially if feed-in tariffs are predicted to stabilise around 5-8 c/kWh nationally through 2025-26.
To ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment, try to compare at least three quotes from reputable installers. The cheapest option isn’t always the best – consider factors like warranty, after-sales service, and the installer’s track record. When comparing quotes, look for details like system size, cell type used, and power output. These considerations will help you navigate the complexities of solar energy costs and make an informed decision about your investment.
What Does a Home Solar System Cost?
System Size and Equipment Costs
The size of your solar system primarily determines its cost. As of May 2025, a 6kW system using quality components that are professionally installed will generally range between $5,200 – $8,700. Larger households or those with higher energy needs might opt for a 10kW system, which ranges from $7,500 to $10,500.

These prices include panels, inverters, and mounting equipment. Premium panels and inverters will push you towards the higher end of these ranges. For instance, top-tier SunPower panels can cost over $700 each, while more budget-friendly options like Jinko are around $130 per panel.
Installation and Labour Costs
Labour costs vary widely depending on your location and installation complexity. Regional installations often incur higher fees due to travel and accommodation expenses for the installation team.
Installation costs typically make up about 10-20% of your total system price. This means for a 6kW system, you might expect to pay between $520 and $1,740 for labour alone.
Permit Fees and Additional Expenses
Permit fees and potential electrical upgrades can add several hundred dollars to your total cost. Some local councils charge higher fees than others, so it’s worth checking with your local authority.
Battery Storage Options
Adding battery storage to your system significantly increases the cost. As of 2025, home battery units typically range from $5,000 to $15,000, depending on capacity and brand. While prices have decreased over the years, batteries remain a substantial investment.
The Clean Energy Council reports that combined large and small-scale renewable capacity added reached approximately 5.9 GW in 2023, indicating growing interest despite the higher upfront cost. This trend suggests that more Australians see the long-term value in energy independence.
Long-term Maintenance Costs
Solar systems are generally low-maintenance, but you should budget for occasional panel cleaning and potential inverter replacement. Most inverters last 10-15 years, so factor in a replacement cost of $1,000 to $2,000 around the decade mark.
To get an accurate cost for your specific situation, try to obtain multiple quotes from accredited installers. Comparing at least three quotes will help ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. With these costs in mind, let’s explore the financial incentives and savings that can offset your initial investment in solar energy.
How Can You Save on Solar Energy Costs?
At Home Owners Association, we understand that the initial cost of solar energy can be substantial. However, numerous financial incentives and savings opportunities can significantly reduce your overall investment. Let’s explore how you can maximise your savings when you go solar.
Federal Solar Incentives
The Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) is a federal program that provides upfront rebates for solar installations. The rebate will decline annually until the scheme ends in 2030. This means you could receive more significant savings if you act sooner rather than later.
State-Specific Solar Rebates
Many Australian states offer additional rebates and incentives. For example, Victoria’s Solar Homes Program offers rebates of up to $1,400 for solar panel systems and up to $3,500 for solar batteries. New South Wales offers interest-free loans of up to $14,000 for solar-battery systems under their Empowering Homes Program.
These state incentives can vary widely and change frequently. We recommend you check with your local government or energy authority for the most up-to-date information on available rebates in your area.
Reduced Electricity Bills
Perhaps the most significant long-term benefit of solar energy is the reduction in your electricity bills. Electrification is projected to reduce average household energy costs by nearly $1,000 per year, or by almost 20% of current spending on energy, by the 2030s.
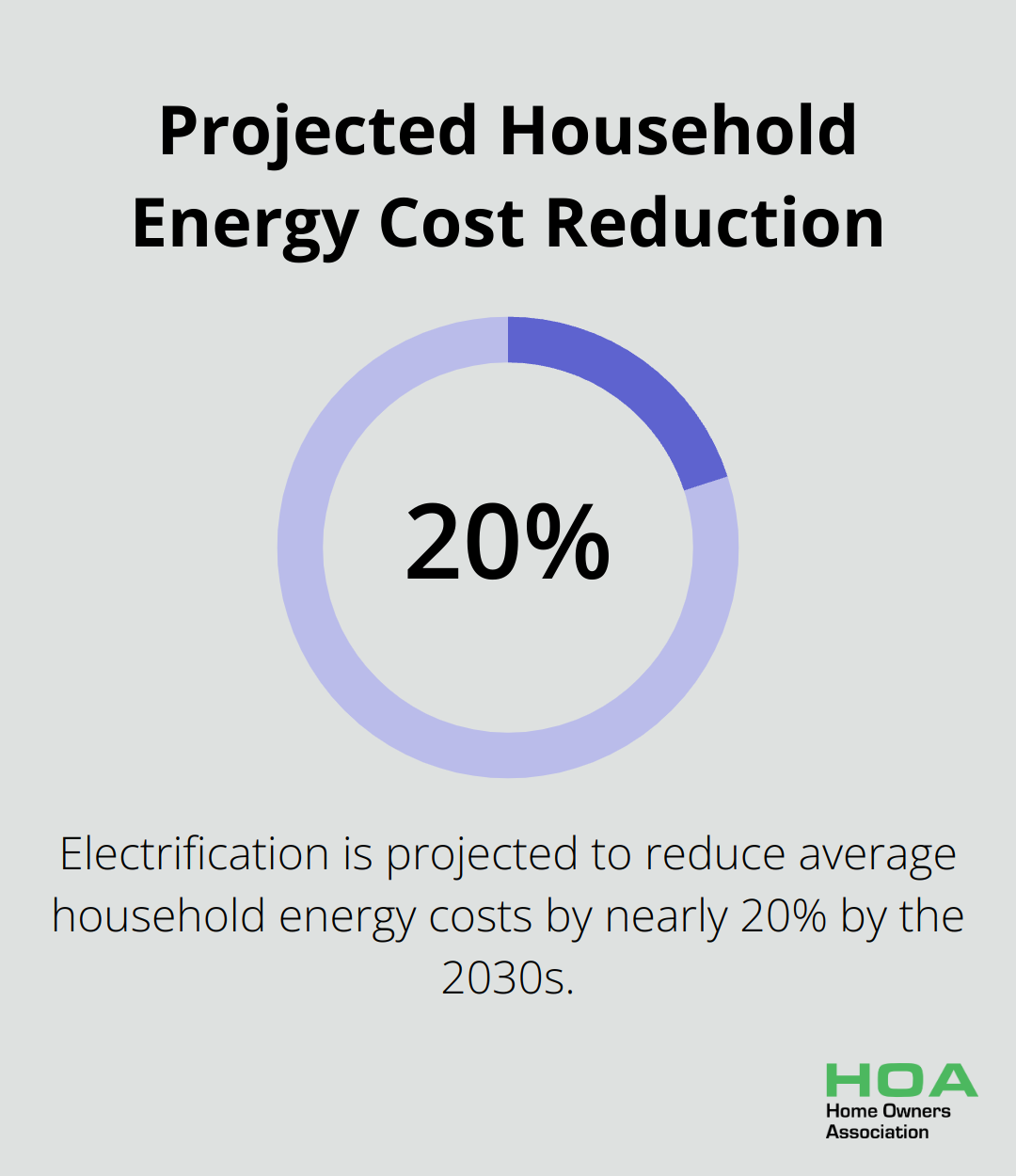
To maximise these savings, you should size your system correctly based on your energy consumption. If you oversize your system, it might lead to excess production that isn’t fully utilised, especially given the relatively low feed-in tariffs across Australia.
Choosing the Right System
When you select a solar energy system, you should consider both your current and future energy needs. A system that’s too small might not provide sufficient savings, while an oversized system could result in unnecessary costs.
Try to obtain quotes from multiple accredited installers (at least three) to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. Compare not just prices, but also the quality of components, warranties, and after-sales service.
You should also consider the long-term performance of your system. While premium panels and inverters might cost more upfront, they often offer better efficiency and durability, potentially leading to greater savings over time.
Final Thoughts
Investing in solar energy for your home requires careful consideration of various cost factors. The price of solar panels, inverters, and installation can vary widely based on your location, roof characteristics, and energy needs. The long-term financial benefits of solar energy are compelling, as you can significantly lower your monthly energy bills by reducing your reliance on grid electricity.
Federal and state incentives offset the upfront costs, making solar more accessible than ever before. The Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme provides immediate rebates, while state-specific programs offer additional savings opportunities. These incentives, combined with the ongoing reduction in electricity costs, contribute to a favourable return on investment for many homeowners.
At Home Owners Association, we emphasise the importance of obtaining multiple quotes from accredited installers to find the best solar energy for home price. This approach helps you make an informed decision that balances cost with long-term performance and reliability. As solar technology advances and electricity prices rise, solar energy becomes an increasingly cost-effective choice for your home.





