
At Home Owners Association, we’re committed to promoting sustainable living practices. Building sustainable homes is a key step towards a greener future.
In this post, we’ll explore eco-friendly building materials, energy-efficient design strategies, and green building certifications. These elements are essential for creating homes that minimise environmental impact while maximising comfort and efficiency.
What Are the Best Sustainable Building Materials?
Sustainable building materials form the cornerstone of eco-friendly homes. The demand for these materials has surged as more homeowners prioritise environmental responsibility. Let’s explore some top choices that can significantly impact your sustainable home project.
Recycled and Reclaimed Materials
Recycled and reclaimed materials revolutionise sustainable construction. The Australian Government’s Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water reports that performance in terms of resource recovery from the C&D stream is highly variable across different Australian jurisdictions.
Reclaimed wood stands out as a popular choice. It offers environmental benefits and adds unique character to homes. Many homeowners successfully incorporate reclaimed wood in flooring, beams, and feature walls.
Recycled steel presents another excellent option. Its strength and durability make it ideal for construction, and it maintains quality through infinite recycling cycles. The World Steel Association states that each tonne of recycled steel saves 1.5 tonnes of iron ore and cuts CO2 emissions by 1.5 tonnes.

Eco-Friendly Insulation Options
Effective insulation plays a vital role in energy efficiency. Natural insulation materials (such as sheep’s wool, cellulose, and cork) have gained traction among environmentally conscious homeowners.
Sheep’s wool insulation excels in performance. This renewable and biodegradable option impresses with its efficiency. Research has shown measurements for the thermal resistance of sheep-wool insulation and wool-hemp mixtures in the form of bonded insulation batts.
Cellulose insulation, derived from recycled paper products, offers another great alternative. Its non-toxic borate treatment provides fire resistance and pest repellent properties. The National Insulation Association reports that cellulose insulation can lower energy bills by up to 25%.
Low-Impact Flooring Choices
For sustainable flooring, bamboo and cork lead the pack. Bamboo’s rapid growth rate (up to 91 cm per day) makes it a highly renewable resource. Its hardness surpasses many hardwoods, making it ideal for high-traffic areas.
Cork flooring has also gained popularity. Harvested from cork oak tree bark without harming the tree, cork boasts natural antimicrobial properties and acts as a thermal and acoustic insulator.
Engineered timber flooring appeals to those who prefer a traditional look. It uses less solid wood than conventional hardwood floors, enhancing its sustainability. Many homeowners report satisfaction with engineered timber floors, citing durability and aesthetic appeal as key benefits.
The selection of sustainable materials marks just the beginning of an eco-friendly construction journey. The next crucial step involves implementing energy-efficient design strategies to maximise the benefits of these materials and create truly sustainable homes.
How to Design Energy-Efficient Homes
At Home Owners Association, we recognise the importance of energy-efficient design in creating sustainable homes. Smart strategies can significantly reduce energy consumption and environmental impact for homeowners.
Harnessing the Power of Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design maximises the use of natural sunlight and heat, which reduces reliance on artificial lighting and heating systems. Passive heating uses free heating direct from the sun to dramatically reduce the cost of heating your home.
To implement passive solar design effectively:
- Position living areas to face north (in the Southern Hemisphere)
- Install large, north-facing windows with appropriate shading devices
- Use thermal mass materials (e.g., concrete floors or brick walls)
Integrating Smart Home Technology for Enhanced Efficiency
Smart home technology revolutionises energy management in Australian homes. These systems allow homeowners to monitor and control their energy usage in real-time, leading to significant savings.
According to a survey, 40% of respondents say they have a smart thermostat, with 27% using it to control energy costs. Additionally, 30% of respondents use a smart meter to control energy costs.
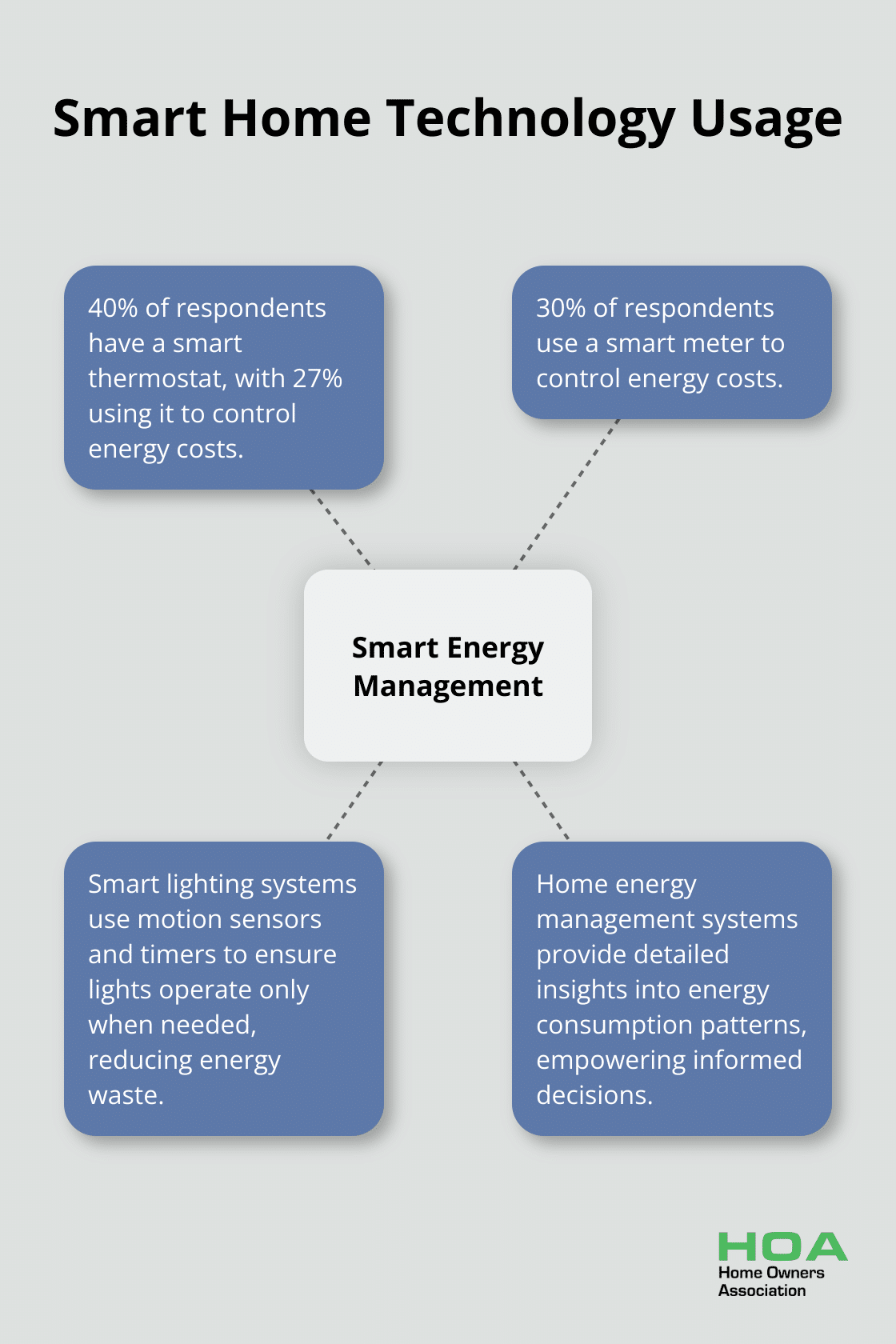
Smart lighting systems use motion sensors and timers to ensure lights operate only when needed.
Home energy management systems provide detailed insights into energy consumption patterns. This data empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about their energy use.
Implementing Water Conservation Systems
Water conservation is critical for sustainable home design, especially in Australia’s often drought-prone climate. Effective water management systems can significantly reduce water consumption and associated energy use.
Rainwater harvesting systems reduce reliance on mains water.
Greywater recycling systems reuse water from sinks, showers, and laundries for garden irrigation or toilet flushing.
Water-efficient fixtures and appliances also play a crucial role. The Water Efficiency Labelling and Standards (WELS) scheme helps consumers identify products that use less water.
These energy-efficient design strategies create sustainable living spaces that are both comfortable and environmentally responsible. The next step in building a truly green home involves obtaining recognised certifications that validate these efforts. Let’s explore the various green building certifications available to Australian homeowners.
Green Building Certifications Explained
Green building certifications validate sustainable construction practices. These certifications measure and recognise environmentally responsible building design, construction, and operation. In Australia, several certification systems are widely recognised by homeowners and builders.
LEED Certification Process
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is an internationally recognised green building certification system. LEED certification is gaining popularity in residential projects across Australia. The LEED certification process includes four levels: Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, based on points earned across various categories.
To obtain LEED certification, homeowners must register their project with the Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA) and submit documentation for review. The process typically takes several months and involves multiple assessment stages. While LEED certification can be complex and expensive, it offers significant prestige and can increase property value.
Green Star Rating System
The Green Star Rating System, developed by the GBCA, is Australia’s most widely used green building certification. It assesses project sustainability across nine categories (including energy, water, materials, and indoor environment quality). The system uses a six-star scale, with six stars representing world leadership in sustainable design.
For homeowners, the Green Star Homes Standard is particularly relevant. This standard focuses on residential properties and aims to create homes that are healthy, resilient, and energy-efficient. To achieve certification, homes must meet minimum requirements in areas such as energy performance, water efficiency, and sustainable materials use. The GBCA reports that Green Star certified buildings use 66% less electricity than average Australian buildings, resulting in significant cost savings for homeowners.

NABERS Energy and Water Ratings
The National Australian Built Environment Rating System (NABERS) measures the environmental performance of existing buildings. While primarily used for commercial buildings, NABERS now includes residential apartment buildings.
NABERS Energy ratings for apartment buildings indicate a building’s operational efficiency. These ratings are valuable for apartment owners and buyers, as they offer insight into potential energy and water bills, and can help reduce carbon emissions and add value to the property.
To obtain a NABERS rating, building owners must engage an accredited assessor who will collect and analyse 12 months of energy and water consumption data. This process typically takes 4-6 weeks and costs vary depending on the size and complexity of the building.
Green building certifications offer tangible benefits for homeowners. They provide a framework for creating sustainable homes, can lead to significant cost savings through improved efficiency, and often result in healthier living environments. As environmental awareness grows, these certifications are becoming increasingly important in the Australian property market.
Final Thoughts
Building sustainable homes is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for a greener future. We explored eco-friendly construction, from sustainable materials to energy-efficient design strategies and green certifications. These practices reduce environmental impact and create healthier, more comfortable living spaces.
The long-term benefits of green homes include significant reductions in energy and water bills, improved indoor air quality, and increased property value. Sustainable homes also contribute to mitigating climate change and preserving natural resources for future generations (a responsibility we all share).
Home Owners Association encourages all homeowners and builders in Melbourne to embrace these eco-friendly approaches. Our team offers expert advice, resources, and benefits to help you navigate your sustainable home projects. We support your journey towards a more sustainable home and work together to make sustainable homes the norm.





